Laser Hair Removal: Precision and Long-Term Results
Laser hair removal has become a sought-after cosmetic procedure, combining advanced technology with non-invasive techniques to achieve semi-permanent hair reduction. Ideal for those seeking smooth, low-maintenance skin, it balances efficiency with evolving safety standards.
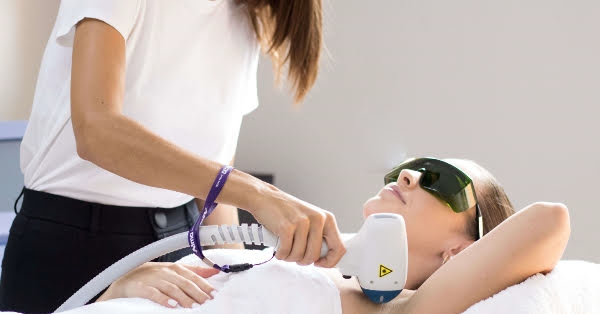
How It Works
The procedure targets melanin in hair follicles using concentrated laser beams. The light energy converts to heat, damaging follicles to inhibit regrowth. Key technologies include:
-
Diode lasers: Effective for most skin types, prioritizing darker, coarse hair.
-
Alexandrite lasers: Faster for large areas (e.g., legs) but better suited for lighter skin tones.
-
Nd:YAG lasers: Safe for darker skin, bypassing melanin in the epidermis to reduce burn risks.
Ideal Candidates
Best results are seen in individuals with high contrast between skin and hair color (e.g., fair skin with dark hair). Modern devices, however, now accommodate diverse skin tones. Those with hormonal imbalances (e.g., PCOS) may require more sessions.
Treatment Process
-
Consultation: Assess skin type, medical history, and expectations.
-
Pre-care: Avoid sun exposure and waxing for 4–6 weeks pre-treatment.
-
Procedure: Sessions last 15–60 minutes, depending on the area. Cooling gels or devices minimize discomfort.
-
Post-care: Apply soothing creams; avoid heat exposure for 48 hours.
Benefits and Considerations
-
Pros: Long-lasting results (80–90% reduction after 6–8 sessions), precision, and minimal downtime.
-
Cons: Temporary redness/swelling; rare risks include burns or pigment changes if improperly administered.
Conclusion
Laser hair removal merges science and aesthetics to deliver convenience and confidence. While not entirely permanent, its efficacy and adaptability make it a cornerstone of modern dermatology. Choosing FDA-approved clinics and experienced practitioners ensures optimal outcomes, reflecting its role as a transformative yet practical beauty solution.
Hot Articles

Break Barriers to Homeownership: No Down Payment, No-Income Verification Mortgages Available Now!

Unlocking Affordable 1-3 Bedroom Apartment Options

Secure Your American Education: 90% More Scholarships Available – Apply for Free Today!

El análisis de datos en la era digital: cómo transforma nuestra vida y decisiones